Geneticists Use ____ to Study the Genetics of Families Through Generations.​
Genetics: The Study of Heredity
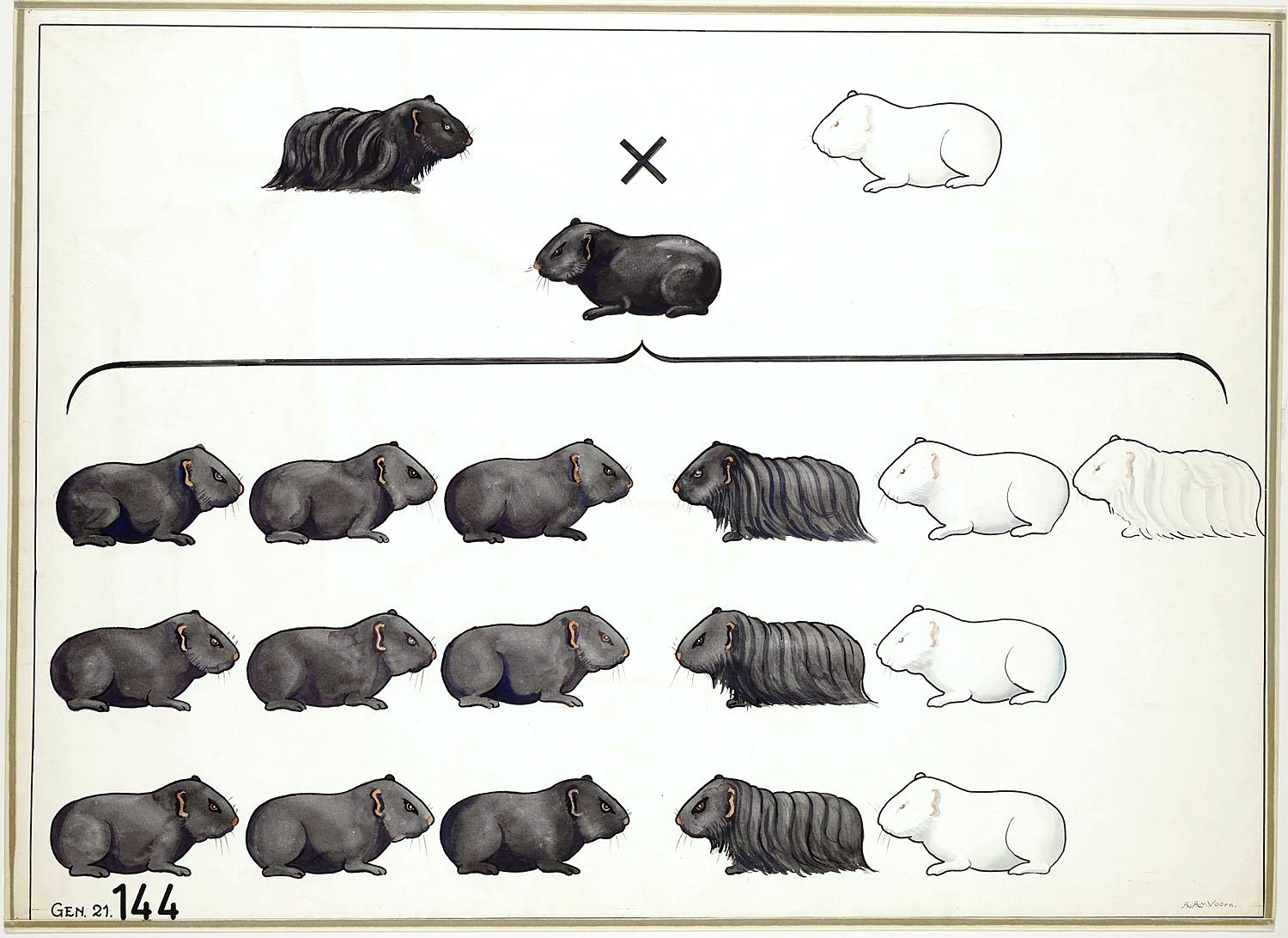
Genetics is the study of how heritable traits are transmitted from parents to offspring. Humans take long observed that traits tend to be similar in families. It wasn't until the mid-nineteenth century that larger implications of genetic inheritance began to be studied scientifically.
Natural choice
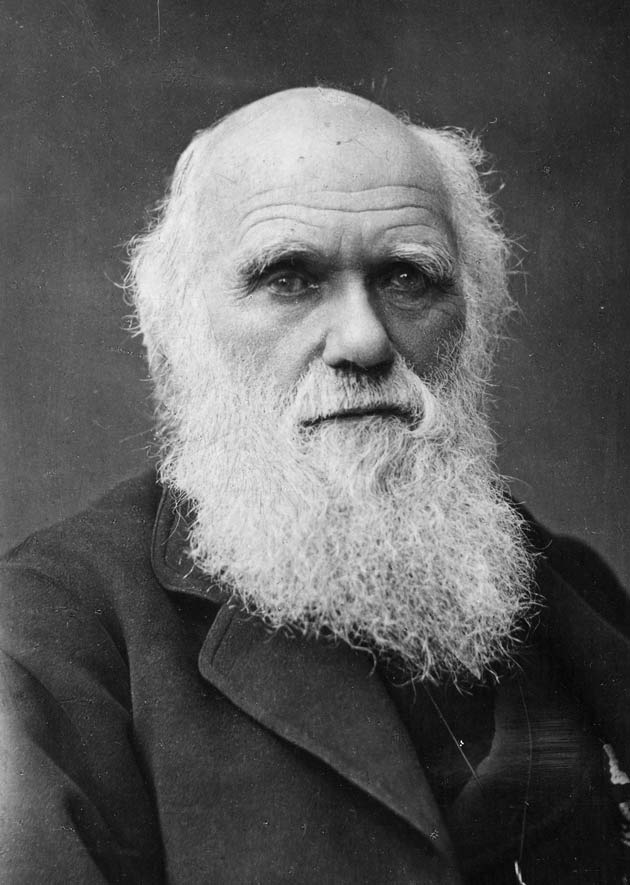
In 1858, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russell Wallace jointly announced their theory of natural option. According to Darwin'south observations, in nearly all populations individuals tend to produce far more offspring than are needed to replace the parents. If every individual born were to live and reproduce still more offspring, the population would collapse. Overpopulation leads to competition for resources.
Darwin observed that it is very rare for any two individuals to exist exactly alike. He reasoned that these natural variations amongst individuals lead to natural selection. Individuals born with variations that confer an advantage in obtaining resources or mates take greater chances of reproducing offspring who would inherit the favorable variations. Individuals with unlike variations might be less likely to reproduce.
Darwin was convinced that natural choice explained how natural variations could lead to new traits in a population, or fifty-fifty new species. While he had observed the variations existent in every population, he was unable to explain how those variations came about. Darwin was unaware of the work being done past a quiet monk named Gregor Mendel.
Inheritance of traits
In 1866, Gregor Mendel published the results of years of experimentation in convenance pea plants. He showed that both parents must pass detached physical factors which transmit data nearly their traits to their offspring at conception. An individual inherits 1 such unit of measurement for a trait from each parent. Mendel's principle of potency explained that most traits are not a alloy of the father's traits and those of the mother as was commonly thought. Instead, when an offspring inherits a cistron for opposing forms of the aforementioned trait, the ascendant form of that trait will be credible in that individual. The factor for the recessive trait, while not apparent, is still part of the individual's genetic makeup and may be passed to offspring.
Mendel's experiments demonstrated that when sex cells are formed, the factors for each trait that an private inherits from its parents are separated into different sex cells. When the sex activity cells unite at conception the resulting offspring will have at least two factors (alleles) for each trait. Ane inherited gene from the female parent and one from the begetter. Mendel used the laws of probability to demonstrate that when the sex cells are formed, information technology is a matter of take chances as to which factor for a given trait is incorporated into a particular sperm or egg.
We now know that uncomplicated say-so does non explain all traits. In cases of co-dominance, both forms of the trait are equally expressed. Incomplete dominance results in a blending of traits. In cases of multiple alleles, there are more than just ii possible means a given gene tin be expressed. We likewise now know that most expressed traits, such as the many variations in human skin colour, are influenced past many genes all acting on the aforementioned apparent trait. In addition, each factor that acts on the trait may accept multiple alleles. Ecology factors can also interact with genetic information to supply even more variation. Thus sexual reproduction is the biggest contributor to genetic variation among individuals of a species.
Twentieth-century scientists came to empathise that combining the ideas of genetics and natural selection could lead to enormous strides in understanding the variety of organisms that inhabit our earth.
Mutation
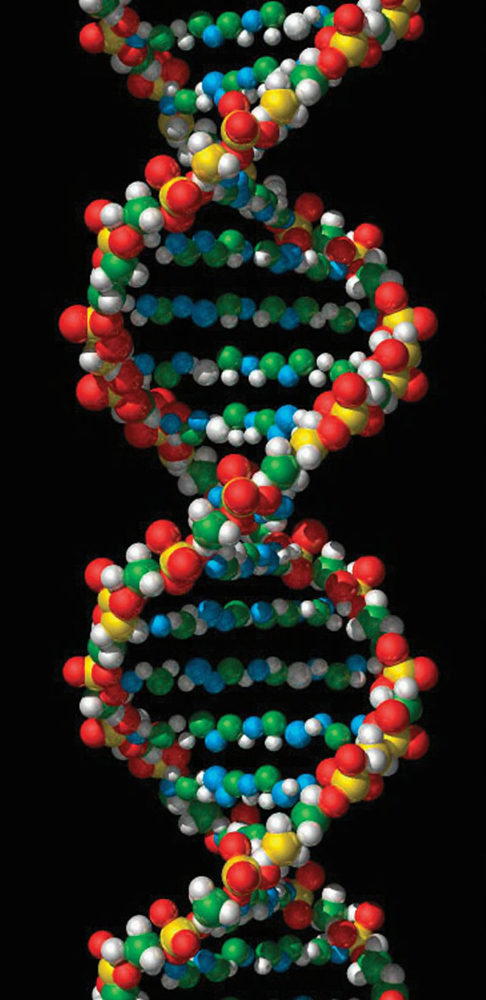
Scientists realized that the molecular makeup of genes must include a way for genetic data to be copied efficiently. Each cell of a living organism requires instructions on how and when to build the proteins that are the basic edifice blocks of body structures and the "workhorses" responsible for every chemic reaction necessary for life. In 1958, when James Watson and Francis Crick described the structure of the Dna molecule, this chemic structure explained how cells employ the information from the DNA stored in the cell'due south nucleus to build proteins. Each time cells divide to form new cells, this vast chemical library must exist copied so that the girl cells have the information required to function. Inevitably, each time the DNA is copied, there are minute changes. Most such changes are defenseless and repaired immediately. However, if the amending is not repaired the change may upshot in an altered protein. Altered proteins may non function normally. Genetic disorders are conditions that result when malfunctioning proteins adversely bear upon the organism. [Gallery: Images of Deoxyribonucleic acid Structures]
In very rare cases the contradistinct poly peptide may function better than the original or result in a trait that confers a survival reward. Such benign mutations are ane source of genetic variation.
Factor menstruation
Some other source of genetic variation is cistron flow, the introduction of new alleles to a population. Commonly, this is due to simple migration. New individuals of the same species enter a population. Environmental conditions in their previous home may accept favored dissimilar forms of traits, for example, lighter colored fur. Alleles for these traits would be different from the alleles nowadays in the host population. When the newcomers interbreed with the host population, they introduce new forms of the genes responsible for traits. Favorable alleles may spread through the population. [Inaugural: Genetics by the Numbers — 10 Tantalizing Tales]
Genetic migrate
Genetic drift is a change in allele frequency that is random rather than being driven by pick pressures. Retrieve from Mendel that alleles are sorted randomly into sex cells. It could just happen that both parents contribute the same allele for a given trait to all of their offspring. When the offspring reproduce they can only transmit the i course of the trait that they inherited from their parents. Genetic drift can cause big changes in a population in only a few generations peculiarly if the population is very small. Genetic migrate tends to reduce genetic variation in a population. In a population without genetic diversity there is a greater chance that ecology change may decimate the population or bulldoze it to extinction.
— Mary Bagley, LiveScience Contributor
Further reading:
- History of Genetics Timeline: AccessExcellence.org
- Kimball's Biology Pages: Development
Source: https://www.livescience.com/27332-genetics.html
0 Response to "Geneticists Use ____ to Study the Genetics of Families Through Generations.​"
Post a Comment