Chinese Reading and Comprehension: a Cognitive Psychology Perspective
Updated
This guide gives you a articulate understanding of how cognitive learning tin can positively impact your life in a corporate environment.
Training of cognitive learning to employees in organizations enhances and strengthens their expertise in handling more than complex tasks.
Discover:
- What is Cognitive Learning?
- Components of Cognitive Learning
- Сognitive Learning Theories
- Cognitive Learning Theory
- Social Cognitive Theory
- Cognitive Behavioral Theory
- Benefits of Cognitive Learning
- Cognitive Learning Strategies
- Cognitive Learning Examples
What is Cognitive Learning?
Cognitive learning is an active style of learning that focuses on helping you larn how to maximize your brain's potential. Information technology makes it easier for y'all to connect new information with existing ideas hence deepening your memory and retention capacity.
The ability of the brain'southward mental processes to blot and retain information through experience, senses, and thought is known every bit cognition.
Employers need to expose employees to training on cerebral learning—an organization whose employees have strong cognitive skills is likely successful.
Well-trained and fully engaged employees are capable of learning speedily and being highly productive by treatment multiple complex tasks without the necessity of a supervisor.
There is a young co-operative of psychology known equally cognitive psychology. It is the study of one's internal processes.
These are the things going on in your brain, such as thinking, attention, learning, trouble-solving, perception, amid others.
Components of Cognitive Learning
Traditional learning mainly focuses on memorization instead of trying to achieve mastery in a detail subject.
The post-obit are primal aspects of cognitive learning:
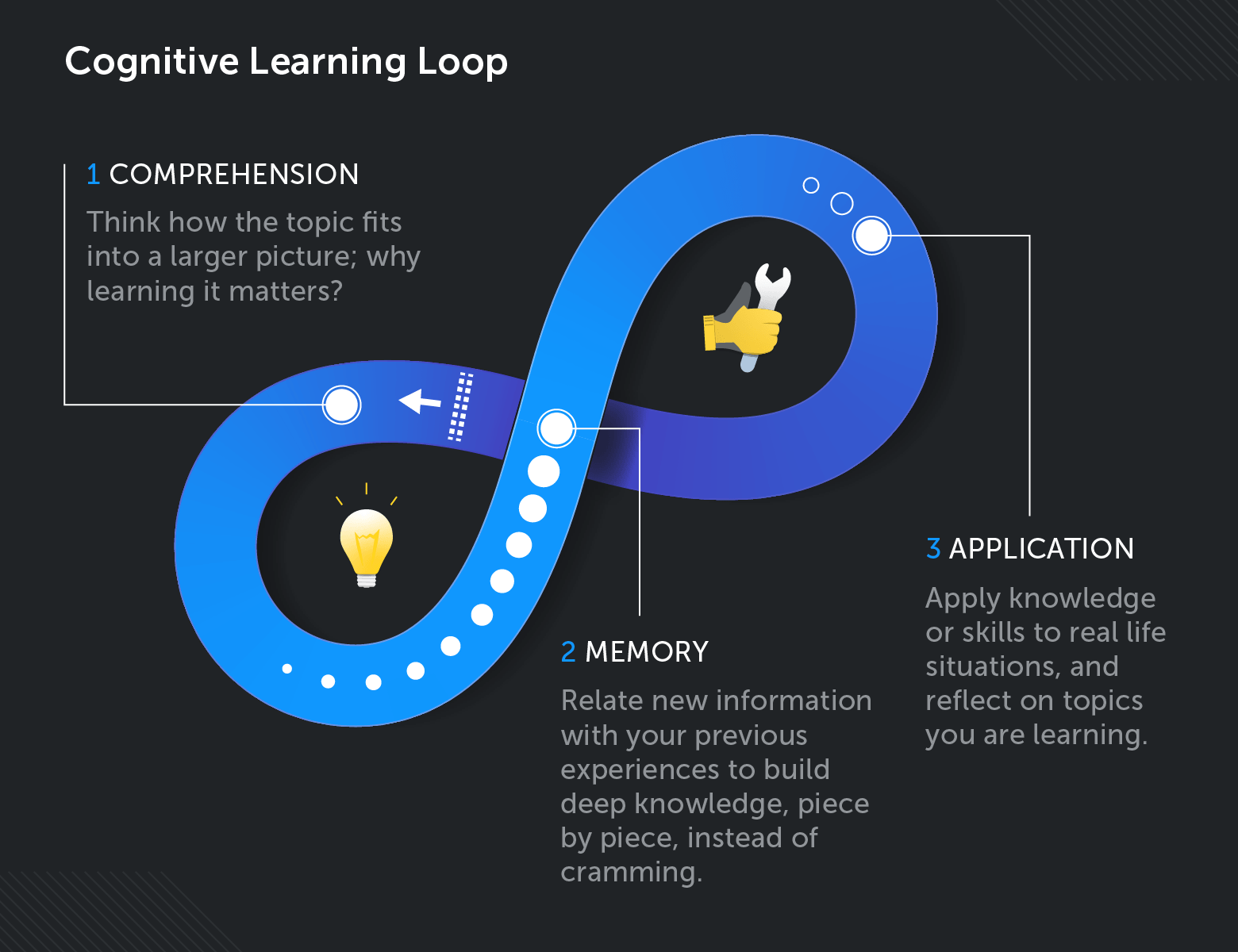
i. Comprehension
For cognitive learning to be efficient and do good you, empathize the reason why you are learning a specific subject in the first place.
2. Memory
Cognitive learning discourages cramming of data, which is very ineffective in instruction. Having a deep understanding of a subject improves your ability to relate new cognition with previous experiences or information.
3. Application
Cognitive learning strategies assistance you utilize new data or skills in life situations. They encourage you equally you continue to develop problem-solving skills.
Сognitive Learning Theories
Cerebral Learning Theory
Cerebral learning theory explains how internal and external factors influence an individual'southward mental processes to supplement learning.
Delays and difficulties in learning are seen when cognitive processes are not working regularly. These processes are such as attention, observation, retrieval from long-term memory, and categorization.
Several researchers accept made pregnant contributions to this theory. Jerome Bruner focused on how mental processes are linked to teaching.
Another researcher by the name Jean Piaget recognized that the environment plays a huge role and also focused on changes that take identify in the internal cerebral structure. You can read more than virtually Piaget's theory of cerebral development in our previous article.
Today, cognitive learning theory is dominant in psychology. It is broken down into ii categories.
This theory helps united states sympathise how people are influenced and their influence on the environment.
One of the major components of social cognitive theory is observational learning. It is the procedure of learning others' desirable and undesirable behaviors through observation.
It is a quick way of acquiring information when yous individually take action. A person who demonstrates behavior for some other person is known equally a model.
These may be real people such as teachers, our peers, and supervisors, or symbolic models, likewise known as fictional characters that influence an observer'southward beliefs.
Observational learning teaches people both positive and negative behaviors. For example, a manager within a visitor can teach the employees how they are supposed to deport ethically and exist socially conscious when interacting and dealing with rude customers. Moreover, the manager can too railroad train his/her employees on the unlike procedures that they can have in case of fire or other low probability hazardous scenarios.
Cognitive Behavioral Theory
This theory mainly refers to our mental processes, such as our thoughts and interpretations of life events.
It explains how the thoughts, feelings, and behavior of a person collaborate with each other. Thoughts lead to detail emotions, which in turn lead to specific behavioral responses.
When we modify our thoughts, nosotros can change our emotions and then our behaviors. It also works in opposite where changing how nosotros behave leads to changes in our feelings and, ultimately, our thoughts.
Let's take an case of a developer who encounters a problem in a particular sphere and automatically believes that the job is hard for him/her right away. The employee is automatically likely to take a negative attitude towards this particular chore, and his operation will likely be poor.
Benefits of Cognitive Learning
The following are the major positive effects of cognitive learning:
one. Enhances learning
Cognitive learning theory enhances lifelong learning. Workers can build upon previous ideas and apply new concepts to already existing knowledge.
2. Boosts confidence
Employees get more than confident in approaching tasks equally they go a deeper understanding of new topics and learn new skills.
3. Enhances Comprehension
Cognitive learning improves learners' comprehension of acquiring new information. They can develop a deeper understanding of new learning materials.
4. Improves problem-solving skills
Cognitive learning equips employees with the skills they need to learn effectively. They are thereby able to develop trouble-solving skills they tin apply under challenging tasks.
5. Help learn new things faster
Through the experience of learning, the employee will be able to recycle and use the same learning methods that worked previously. This will help them learn new things a lot faster every bit they already know what works for them when it comes to obtaining new noesis.
6. Teaches to grade concept formation (call back abstract)
Cerebral learning can besides teach your employees to class a range of unlike concepts such every bit easily perceiving and interpreting information that could boost creativity and lead to innovations at the workplace.
Cognitive Learning Strategies
Several psychologists have shaped the concept of cognitive learning through inquiry. They came upwardly with theories and learning strategies that can be implemented in a corporate learning environment.
Learner-centered strategy
Jean Piaget termed learning as relating data to already existing knowledge. And each learner starts with their own knowledge and experience.
According to his theories, learning begins with the aggregating of some basic knowledge and advancing deeper into the field with fourth dimension.
Piaget suggested 3 vital components of learning:
- Accommodation - taking new information into account past modifying what nosotros already know.
- Assimilation - the system of new knowledge within our heads abreast what nosotros know.
- Equilibration - balancing what we already know with the new information that we are trying to acquire.
Each company should develop their preparation programs with a personalized learning approach to make information technology engaging for their employees to achieve better results.
To achieve that L&D professionals should focus on the post-obit points:
- Develop and introduce their programs based on already existing noesis.
- Provide more than analogies to connect new noesis with already existing knowledge.
- Divide learning materials into stages and maintain a logical menstruation of lessons taught.
- Provide examples or applied tasks that show how new information or principles tin connect with previous knowledge, or enhance it.
- Encourage questions and comments from trainees.
Meaningful Experiences strategy
David Ausubel fabricated a clear distinction between meaningful learning and rote learning.
According to him, material that was closely related to what the learner knew was meaningful and always turned out to be effective.
Learners with relevant background knowledge find it easier to add new information.
During the training of learners in an organization:
- There should be an accent on the meaningfulness of each session to the task at hand.
- Background information on new cloth is essential.
- New data should be instilled in learners in a sequence to build on what is already understood.
Learning Through Discovery strategy
Jerome Bruner is a psychologist who built his theory on top of Piaget's theory of cognitive development that was focusing on learning through discovery.
His theory identified iii stages of cognitive representation which are enactive, iconic, and symbolic. Enactive defining the representation of noesis through actions, iconic being the visual summarization of images, and symbolic which is the use of words and symbols to describe experiences.
Through his study of cognitive learning in children, he suggested that they should exist allowed to discover information for themselves. He believed that learners review previously learned material fifty-fifty equally they gain new noesis.
His interpretation of Cognitive Learning Theory in a corporate surroundings can be put by:
- Allow employees to larn new skills and get new knowledge through new tasks and challenges.
- Challenge trainees to solve real-world problems your system faces.
Personalized learning strategy
All of these strategies can be combined into one personalized learning arroyo. Each learner is unique and has their ain feel, knowledge, and perception. Which can greatly influence the way they translate and consume new information.
Creating learning experiences that fit each individual based on their own knowledge that is meaningful for their role which encourages them to discover new solutions tin can drive peachy results and improve their overall performance.
Fifty&D professionals should effort to organize a learning environment, to let employees to larn at their ain step, and with a variety of learning opportunities.
A common practice in recent years to create personalized learning is the use of modern technologies: AI recommendations, learning paths, machine learning, natural language processing.
For example, a digital learning banana has the capability to recognize what the skills of the employees are, what they have learned so far, and automatically propose to them what they should learn next. The reason why such modern applied science is essential in employee development, considering it tin offer information they need without them fifty-fifty anticipating the need for it. Overall, it's a fantastic tool that can ensure better employee didactics and eventually drive greater performance.
Moreover, the visitor can save a significant amount of resource with a learning banana equally it can make your organization'south learning environs flawless even if scalability is required.
Furthermore, having the ultimate access to a range of company resources, no two employees need to learn or go through the same learning process as they can cherry-choice what they want to learn from.
Cognitive Learning Examples
Now yous have a clear thought of what cognitive learning means. The post-obit are diverse examples of cognitive learning.
1. Explicit Learning
Information technology happens when you intentionally seek knowledge to attempt and learn a new skill or process that may be vital to your work. It requires yous to be attentive and take action to acquire knowledge.
An example of explicit learning would be undertaking an in-depth video editing course to understand the functionality of the software in gild to exist able to use it appropriately for the needs of your piece of work.
2. Implicit Learning
Sometimes you passively gain new knowledge and learn some new skills. Information technology is known as implicit learning, where you lot are unaware of the entire procedure until yous realize y'all accept retained something new.
This blazon of learning may occur when you are working, talking, or going near your normal life.
Typing fast and without looking at your keyboard is one good instance of implicit learning that comes automatically over fourth dimension.
3. Meaningful Learning
Meaningful learning is when you are capable of acquiring new information and relating it to past experiences.
This is considering this cognitive learning approach teaches employees to build transferable problem-solving skills that tin be applied in other areas.
An instance of meaningful learning is when y'all work in procurement and decide to have an advanced course in your department to deepen your agreement of the subject.
iv. Discovery Learning
It happens when y'all actively seek new noesis by researching new concepts, processes, and subjects.
For case, if someone is ready the task to proofread a detail report and they need to make use of a specific tool such as Grammarly, past using this tool in hand with the manuals, this would cause them to larn the features and abilities of the tool through discovery.
5. Receptive Learning
Lectures where you sit in groups and a speaker feeds the audience with information on a specific subject is an case of receptive learning. It requires the learner to be active by request questions and taking down short notes.
During training in your workplace, this type of learning comes in handy where you lot get a deeper agreement of new information by being agile and responsive to the speaker.
6. Non-Associative Learning (Habituation and Sensitization)
It is a type of learning that enables humans to adjust to something by facing it frequently.
When you become a new job at a mill where there are many machines making noise, it irritates for the get-go few days, but you later learn how to live with it. This is known as habituation.
Sensitization is the vice versa whereby your reaction towards something increases as y'all get frequent exposure towards it.
This blazon of learning happens in your typical situations in life and work. Working in an office teaches you to exist more than responsive to things like telephone calls.
seven. Emotional Learning
Developing emotional intelligence is crucial to help the states maintain friendly relationships with friends at piece of work and in life.
Emotional learning helps people larn how to take charge of their emotions and also understand others'.
An employer requires to have command over their emotions so every bit to handle customers and also their superiors in a courteous manner.
8. Experiential Learning
Our experiences in life are our best lessons.
Your interactions with other people always teach you some precious life lessons. What you acquire depends on how you interpret information technology.
For case, an intern learns past shadowing an experienced senior employer to gain feel. He acquires new skills that are relevant to his line of piece of work.
9. Observation Learning
Ane of the significant components of the social cognitive theory is observational learning.
It is handy amidst employees since it mainly involves imitation of skills from colleagues and superiors.
Observing your friends or work colleagues is an efficient way to larn a new skill.
Your successful manager at work can help y'all ameliorate your leadership qualities as you encompass and practice his habits.
10. Cooperative and Collaborative Learning
Working and learning in groups is encouraged in many institutions.
Cooperative learning helps bring out one's best skills and deepens the collaboration between a group of people (read more well-nigh collaborative learning).
However, for an individual to learn this manner, he/she has to be an agile and equal participant and interact with young man group members.
Some companies select individuals to train on new strategies that improve the success of an organization. The trained employees are then encouraged to pass on this cognition to their team members.
The types of cognitive learning above are vital in using your brain's features equally much every bit possible. They make it easier for yous to acquire new skills and knowledge in life.
Source: https://www.valamis.com/hub/cognitive-learning
0 Response to "Chinese Reading and Comprehension: a Cognitive Psychology Perspective"
Post a Comment